
प्रश्न आधारभूत मनोवैज्ञानिक प्रक्रियाएं
(अ) संवेदनाः संवेदना से तात्पर्य उन विभिन्न उत्तेजनाओं के प्रति हमारी जागरूकता से है जो
हमें विभिन्न संवेदीतंत्रों द्वारा प्राप्त होती हैं जैसे, दृष्टि, श्रवण, स्पर्श, गन्ध तथा स्वाद।
(ब) अवधानः अवधान के समय हम उपलब्ध कई उत्तेजनाओं में से किसी एक विशेष उत्तेजना पर चयनात्मक रूप से केन्द्रित होते हैं, उदाहरणतः कक्षा में व्याख्यान सुनते समय हम शिक्षक द्वारा बोले गये शब्दों को सुनते हैं तथा कक्षा में उपस्थित अन्य उत्तेजनाओं को नजर अंदाज करते हैं, जैसे पंखे का शोर।
(स) प्रत्यक्षीकरणः प्रत्यक्षीकरण में हम सूचना को संसाधित करते हैं और उपलब्ध उत्तेजनाओं का अर्थ निकालते है। उदाहरण के लिये, जब हम एक पेन को देखते हैं तो हम उसे एक लिखने वाली वस्तु के रूप में पहचानते हैं।
(द) सीखना (अधिगम): ये अनुभव और अभ्यास द्वारा नये ज्ञान और कौशलों के अर्जन में हमारी सहायता करता है। ये अर्जित ज्ञान और कौशल हमारे व्यवहार में अपेक्षित परिवर्तन लाते हैं और विभिन्न परिस्थितियों में समायोजन करने में हमारी सहायता करते हैं।
(य) स्मृतिः जो सूचना हम संसाधित करते हैं और सीखते हैं, उसका हमारे स्मृतितन्त्र में धारण हो जाता है। आवश्यकता पड़ने पर धारित सूचना का पुनरोत्पादन करने में भी स्मृति हमारी सहायता करती है। उदाहरण के लिये, परीक्षा के लिये अध्ययन करने के पश्चात् प्रश्न पत्र में दिये गये प्रश्नों के उत्तर लिखना।
(फ) चिंतनः चिंतन के अन्तर्गत हम धारण किये गये ज्ञान का विभिन्न समस्याओं के समाधान में प्रयोग करते हैं। जब भी हमारे सामने कोई समस्या आती है, तब हम अपने मन में, उस समस्या से जुड़े विभिन्न तथ्यों का एक दूसरे से तर्कपूर्ण सम्बन्ध स्थापित करते हैं और तब समस्या के सम्बन्ध में एक विवेकपूर्ण निर्णय लेते हैं।
Basic Psychological Processes
(A)Sensation: It refers to our awareness about various stimuli which we encounter in different modalities such as vision, hearing, touch and taste.
(B) Attention: During attention we selectively focus on a particular stimulus among many stimuli available to us. For instance while listening to a lecture in the classroom we attend to the words pronounced by the teacher and, try to ignore the other stimuli present in the classroom, such as noise made by the fan.
(C)Perception: In the case of perception we process information and make out the meaning of the stimuli available to us. For example, wo look at a pan and recognize it as an object used for writing.
(D)Learning: It helps us acquiring new knowledge and skills through experience and practice. The acquired knowledge and skills further bring a relative change in our behavior and facilitate our adjustment in varied settings. For example, we learn language, riding a bicycle and applying mathematical skills to solve various problems.
(E) Memory: The information we process and learn is registered and stored in the memory system. Memory also helps us to easily retrieve the stored information when it is required for use. For example, writing the answers in the examination after studying for the paper.
(F) Thinking: In the case of thinking we use our stored knowledge to solve various tasks. We logically establish the relationships among various objects in our mind and take rational decision for a given problem.
प्रश्न स्मृति के प्रकार
मनोवैज्ञानिकों ने स्मृति को निम्नलिखित चार प्रकारों में बांटने की संकल्पना की।
शब्दार्थ विषयकः यह ज्ञान, अर्थ और सामान्यीकृत अनुभवों से सम्बन्ध रखता है। जो भी हम किताबों से याद करते हैं, चारों ओर की घटनाओं की सूचनाएं, शब्दों के अर्थ इसमें शामिल किये जाते हैं।
वृत्तात्मकः यह व्यक्ति के व्यक्तिगत अनुभवों को इंगित करता है। आप दिन में कई कार्य करते हैं। आपको अनोखे अनुभव होते हैं। स्मृति के ऐसे अनुभवों में सिर्फ आप पहुँच सकते हैं। यह आपकी वृत्तात्मक स्मृति का भाग हैं।
प्रक्रियात्मकः यह स्मृति के उस भाग से सम्बन्ध रखता है जिसमें किसी कार्य को करने या उसे प्रदर्शित करने के तरीके आते हैं।
तत्व स्मृतिः यह स्मृति आपकी स्मृति के लिए है। हम सूचनाओं को याद ही नहीं रखते अपितु यह भी याद रखते हैं कि हम सूचनाओं को याद रख सकते हैं। लोग अपनी स्मृतियों को समझने में खुद ही अच्छे व बुरे हो सकते हैं।
Types of Memory
Psychologists have conceptualized memory into four types as given below:
Semantic : This deals with knowledge, meaning and generalized experiences. What ever we remember from books and information about world events and meanings of words are included in it.
Episodic : It refers to the experiences which are personal to an individual. You do so many things in a day. They are your unique experiences. Memory of such experiences is accessible by you only. They are part of your episodic memory.
Procedural : This deals with memory for actions or ways of doing certain things or performing certain activities.
Meta Memory : It is memory for your memory. We not only remember things but also remember that we can remember. People may be good or poor in understanding their own memories.
प्रश्न स्मृति को बढ़ाने के उपाय
स्मृति को बढ़ाने के लिए निम्नलिखित उपाय दिए हुए है
➛ गहन प्रक्रम
➛ सावधानीपूर्वक ध्यान देना
➛ हस्तक्षेप को कम करना
➛ विभाजित अभ्यास
➛ स्मृति सहायकों का प्रयोग करें
➛ गुप्त संक्षेप लिपि
Strategies for enhancing memory
Following are the remedies to increase memory
➛ Deep Processing
➛ Attending carefully
➛ Minimize interference
➛ Distributed practice
➛ Using memory aids
➛ Shorthand codes
प्रश्न सृजनात्मकता किसे कहते है ?
सृजनात्मकता (Creativity) सामान्य रूप से जब हम किसी वस्तु या घटना के बारे में विचार करते हैं तो हमारे मनमस्तिष्क में अनेक प्रकार के विचारों का प्रादुर्भाव होता है। उत्पन्न विचारों को जब हम व्यावहारिक रूप प्रदान करते हैं तो उसके पक्ष एवं विपक्ष, लाभ एवं हानियाँ हमारे समक्ष आती हैं। इस स्थिति में हम अपने विचारों की सार्थकता एवं निरर्थकता को पहचानते हैं। सार्थक विचारों को व्यवहार में प्रयोग करते हैं। इस प्रकार की स्थिति सृजनात्मक चिन्तन कहलाती है।
What is creativity?
Creativity: Normally, when we think about an object or event, many types of thoughts arise in our mind. When we give practical form to the ideas generated, then its pros and cons, advantages and disadvantages come before us. In this situation we recognize the significance and futility of our thoughts. Use meaningful ideas in practice. This type of situation is called creative thinking.
प्रश्न सृजनशील व्यक्ति की विशेषताएं –
मनोवैज्ञानिकों ने सृजनशील व्यक्ति की विशेषताओं को समझने के लिए अनेक अध्ययन किये जिसमें मुख्य रूप से व्यक्तित्व परीक्षणों तथा जीवन के अनुभवों का प्रयोग किया गया। मेकिनन तथा उनके सहयोगियों ने वैज्ञानिकों, आविष्कारकों तथा विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में कार्य करने वाले लोगों का अध्ययन करके कुछ गुणों का निर्धारण किया।
➛ कम बुद्धि वाले व्यक्तियों में सृजनात्मकता चिन्तन नही के बराबर होता है।
➛ सृजनशील व्यक्तियों में अन्य व्यक्तियों की अपेक्षा वातावरण के प्रति संवेदना अधिक पायी जाती है।
➛ सृजनशील व्यक्तियों के विचारों तथा क्रियाओं में स्वंत्रता देखी जाती है।
➛ ये व्यक्ति किसी भी घटना, चीज व वस्तु को गंभीरता से नही होते है वरन् प्रत्येक कार्य को मनोविनोद से करते हैं।
➛ सृजनशील व्यक्ति किसी भी विषय पर अधिक विचार व्यक्त करते है।
➛ सृजनात्मकता व्यक्तियों में अन्य व्यक्तियों ज्यादा लचीलापन पाया जाता है।
➛ सृजनात्मकता विचारको में हमेशा एक नवीन जटिल समस्या का समाधान करते हैं। चिन्तन के आधार पर नयी चीज व घटना की खोज करते है।
➛ सृजनशील व्यक्ति अपनी इच्छाओं का कम से कम दमन करते हैं। ऐसे व्यक्ति इस बात की परवाह नही करते हैं कि दूसरे ➛ व्यक्ति क्या सोचेंगे तथा वे अपनी इच्छाओं तथा आवेगों का आदर करते है।
➛ सृजनशील व्यक्ति अपने विचारों को खुलकर अभिव्यक्त करते हैं तथा उन्हें तर्कपूर्ण तरह से प्रस्तुत करते हैं।
➛ सृजनशील व्यक्ति रूढ़िवादी विचारों को सन्देह की दृष्टि से देखते हैं।
➛ सृजनात्मकता व्यक्ति विभिन्न प्रकार की बाधाओं को दूर करते हुए धैर्यपूर्वक अपना कार्य करते हैं।
➛ सृजनात्मकता व्यक्तियों में अपने कार्य के प्रति आत्मविश्वास पाया जाता है ऐसे व्यक्ति लक्ष्य के प्रति संवेदनशील होते है।
Characteristics of a creative person
Psychologists conducted many studies to understand the characteristics of a creative person, mainly using personality tests and life experiences. McKinnon and his colleagues determined certain properties by studying scientists, inventors and people working in different fields.
➛ Creativity thinking is negligible in people with low intelligence.
➛ Creative people have more sensitivity towards the environment than other people.
➛ Freedom is seen in the thoughts and actions of creative people.
➛ These people do not take any event, thing or thing seriously, but do every work with pleasure.
➛ Creative people express more views on any subject.
➛ Creativity individuals have more flexibility than other individuals.
➛ In creativity thinkers always solve a new complex problem. On the basis of thinking, they discover new things and events.
➛ Creative people suppress their desires the least. Such persons do not care about what other people will think and they respect their own desires and impulses.
➛ Creative people express their ideas openly and present them logically.
➛ Creative people view conservative ideas with suspicion.
➛ Creativity individuals do their work patiently, overcoming various types of obstacles.
➛ Creativity is found in individuals with confidence in their work, such people are sensitive towards the goal.
प्रश्न पालने के तरीकों का प्रभाव बच्चे के सामाजीकरण पर क्या पड़ता है।
पालने के मुख्य 4 तरीके हैं:
1. अधिकारपूर्ण तरीका : मांग करना, नियंत्रण करना, गहन पालन करना।
2. अनुज्ञात्मक : (तुष्ट होना), बिना किसी मांग के पालन करना।
3. अधिकारिक तरीका : दृढ़, सतत पालन, अनुशासन के कारण बताना।
4. उपेक्षापूर्ण या असंलग्न तरीका : अरुचिपूर्ण चिन्तारहित, कम नियंत्रण और वार्तालाप।
What is the effect of parenting methods on the socialization of the child.
There are 4 main types of parenting styles:
1. Authoritarian style: demanding, controlling, insensitive parenting
2. Permissive style: indulgent, non-demanding parenting
3. Authoritative style: firm, consistent parenting, reasons given for discipline.
4. Neglectful or uninvolved: style disintersted uncaring, low control and communication.
प्रश्न मध्य बाल्यावस्था किसे कहते है ?
मध्य बाल्यावस्था (आयु 6-12) अपने मध्य बचपन के वर्षों (6 से 12 वर्ष की आयु के बीच) में एक बच्चे का विकास पथ किशोरों के लिए महत्वपूर्ण योगदान देता है, और वे वयस्क हो जाएंगे। मध्य बाल्यावस्था एक ऐसी अवस्था है जहाँ बच्चे विस्तृत भूमिकाओं और परिवेशों की ओर बढ़ते हैं।
What is middle childhood?
Middle Childhood (Ages 6-12) A child’s developmental path in their middle childhood years (between 6 and 12 years of age) contributes substantially to the adolescent, and adult they will become. Middle childhood is a stage where children move into expanding roles and environments.
प्रश्न प्रौढ़ता की कुछ अवधियाँ हैं:
➛ युवा प्रौढ़ता (20 से 30 वर्ष)
➛ मध्य प्रौढ़ता (40 से 50 वर्ष)
➛ अन्तिम प्रौढ़ता (60 वर्ष से ऊपर)
Some periods of maturity are:
➛ Young adulthood (20 to 30 years)
➛ Middle Maturity (40 to 50 Years)
➛ Late Maturity (Above 60 Years)
प्रश्न युवा प्रौढ़ता के लक्षण
➛ आजीविका का चयन।
➛ पारिवारिक जीवन का प्रारम्भ।
➛ समकक्ष लोगों (पीयर्स) से घनिष्ठ सम्बन्ध बनाना।
➛ समाज के प्रति सरोकार।
Signs of young adulthood
➛ Selection of livelihood.
➛ Beginning of family life.
➛ Build closer relationships with peers.
➛ Concern towards society.
प्रश्न अधेड़ प्रौढ़ावस्था के लक्षण
➛ सामर्थ्य, परिपक्तवा, दायित्वधारण, स्थिरता।
➛ संतान के प्रति केन्द्रित-ध्यान।
➛ वृद्धावस्था की योजनायें।
➛ महिलाओं में रजोनिवृत्ति।
Characteristics of Young Adulthood
➛ Choice of a career.
➛ Starting a family life.
➛ Forming close relationships with peers.
➛ Concerns about society.
प्रश्न अधेड़ प्रौढ़ावस्था के लक्षण
➛ सामर्थ्य, परिपक्तवा, दायित्वधारण, स्थिरता।
➛ संतान के प्रति केन्द्रित-ध्यान।
➛ वृद्धावस्था की योजनायें।
➛ महिलाओं में रजोनिवृत्ति।
Characteristics of Middle Adulthood
➛ Competence, maturity, responsibility and stability.
➛ Attention focused on children.
➛ Plans for old age.
➛ Occurrence of menopause in women.
प्रश्न दीर्घ आयु तथा स्वास्थ्य जीवन की कुंजी
(क) पौष्टिक आहार लें।
(ख) नियमित व्यायाम करें।
(ग) तनाव के स्तर को कम करें।
(घ) धूम्रपान, मदिरापान तथा अन्य मादक वस्तुओं का सेवन न करें।
(ङ) सकारात्मक सोच की आदल डालें।
(च) सामाजिक कल्याण के कार्य में संलग्न रहें।
(छ) आध्यात्मिकता तथा ईश्वर में आस्था विकसित करें।
Key to Longer and Healthier Life
(a) Eat healthy diet.
(b) Exercise regularly.
(c) Reduce stress level.
(d) Don’t smoke or drink alcohol and other drugs.
(e) Cultivate certain positive qualities.
(f) Engage with activities of social welfare.
(g) Develop spirituality and faith.
प्रश्न संप्रेषण के तत्त्व
संप्रेषण के मूल तत्त्व इस प्रकार हैं:
i. संप्रेषण द्विपक्षीय प्रकिया है: इसमें भेजने वाला और प्राप्तकर्ता दोनों शामिल होते हैं। जब आप अपने पिता से बात करते है, तब संप्रेषण व्यक्तिगत स्तर पर होता है। जब अध्यापक छात्रों के एक समूह से बात करता है, तो वहाँ संप्रेषण समूह स्तर पर होता है।
ii. उसमें एक संदेश होता है: सूचना हमेशा किसी संदेश, विचार, भावना, मार्गदर्शन या धारणा के रूप में होनी चाहिए।
iii. समझ में समानताः संप्रेषण तभी संभव है जब भेजने वाले एवं प्राप्तकर्ता में समझ की समानता हो। समानता का आधार संस्कृति, भाषा, तथा वातावरण हो सकते हैं। शब्द, पदबंध, मुहावरे, चेष्टायें तथा कहावतें भी संप्रेषण के लिए समान आधार प्रदान करते हैं।
iv दूसरे लोगों के व्यवहार में बदलाव लानाः जो सूचना प्राप्तकर्ता तक भेजी जाती है, वह कहीं न कहीं उसके व्यवहार में कुछ न कुछ परिवर्तन लाती है। उदाहरण के रूप में, जैसे ही आपको पता चलता है कि बिल्डिंग में आग लग गयी है, उसी समय तुरन्त आप
और लोगों के साथ वहां से भाग खड़े होते हैं।
v. सूचना देने की विधिः सूचना शब्दों, चेष्टाओं, अभिव्यक्ति आदि द्वारा प्रदान की जाती है।
Elements of communication
The key elements of communication are:
i. Communication is a two-way process: It involves a sender and a receiver. When you talk to your father, communication is at the individual level. When a teacher talks to a group of students, communication is at group level.
ii. There has to be a message: The information has to be in the form of a message, a directive, an idea, a feeling or an opinion.
iii. Commonness of understanding: Communication can occur only when there is commonness of understanding between sender and receiver. The basis of commonness can be culture, language, and environment. Words, phrases, idioms, gestures and proverbs provide common basis for communication.
iv. Modifying the behavior of other people: The information transmitted to the receiver brings forth a response in the form of some change in his/her behavior. For example, the moment you hear that fire has broken out in the building, you along with others will run out of the building.
v. Method of giving information: Information is provided with the help of words or through gestures, expressions and the like.
प्रश्न संप्रेषण के प्रकार
संप्रेषण को मुख्य रुप से दो भागों में बांटा जा सकता है:
1. मौखिक संचार 2 अमौखिक संचार
मौखिक संप्रेषण:
जब दो या दो से अधिक लोगों के बीच शब्दों का प्रयोग बातचीत के लिये किया जाए, तब उसे मौखिक संप्रेषण कहते हैं। यह लिखित व मौखिक दोनों रूप में हो सकता है। मौखिक संप्रेषण हमें लोगों के बीच तर्कपूर्ण बातचीत के साथ-साथ जानकारी तथा दिशा भी प्रदान करता है। यह हमारे जीवन की मूलभूत जरुरत है। शोधकर्ताओं ने यह पाया है कि लोग सामान्यतः एक दिन के 10 से 11 घंटे मौखिक संप्रेषण में लगाते हैं, जिसमें पढ़ना, बोलना, लिखना तथा सुनना आता है। मौखिक संप्रेषण के कुछ सामान्य रूप बातचीत, भाषण, पत्र, समाचार-पत्र, पत्रिकाएँ, फोन पर होने वाली बातचीत आदि हैं।
अमौखिक संप्रेषण: यहां ध्यान देना बहुत आवश्यक है कि अमौखिक संप्रेषण या हाव-भाव, पूरे संप्रेषण का 70 प्रतिशत भाग होता है, जबकि शब्द केवल 10 प्रतिशत । इसलिए मानवीय संप्रेषण के लिए अमौखिक संप्रेषण बहुत महत्वपूर्ण है। शारीरिक चेष्टाए, चेहरे के हाव भाव, शारीरिक मुद्राएँ, नेत्र सम्पर्क, आसन, शारीरिक उन्मुखता, दूरियाँ आदि कुछ अमौखिक संप्रेषण के रूप हैं।
Types of communication
Communication can be broadly divided into two categories. These are:
1. Verbal communication, and
2. Non-verbal communication.
1. Verbal communication – When words are used as tools of interaction between two or more individuals, it is termed as verbal communication. It can be oral or written. Verbal communication provides us with meaningful interaction between people, information and direction. It is a fundamental requirement for life. Researchers have noted that on an average a person spends 10 to 11 hours every day in verbal communication that is, reading, speaking, writing, or listening. Some common forms of verbal communication are conversations, speeches, letters, newspapers, magazines, telephonic conversations, etc.
2. Non-verbal Communication – It is interesting to note that non-verbal communication or body language, accounts for more than 70 percent of our communication while words account for just about 10 percent ! Thus non-verbal communication is very important in human interaction. Gestures, eye contact, facial expressions, posture and body orientation, distance are some of the non-verbal ways of communicating.
प्रश्न अमौखिक संप्रेषण कैसे मदद करते हैं:
अमौखिक संप्रेषण कैसे निम्नलिखित मदद करते हैं:
➛ मौखिक संप्रेषण के तत्त्वों से हटकर प्रभाव बनाना;
➛ जो कहा गया उसे दृढ़तर करना;
➛ हमारी भावनाओं तथा अन्तरवैयक्तिक मनोवृत्ति को प्रकट करना;
➛ शक्ति, स्नेह, सम्मान, प्रभुता को प्रकट करने में सहायक;
➛ दूसरे के साथ होने वाली बातचीत को व्यवस्थित व नियंत्रित करना, और
➛ आत्म-प्रस्तुतिकरण में सहायक।
How non-verbal communication helps
Non-verbal communication helps to
➛ create impressions beyond the verbal element of communication,
➛ reinforces what has been said,
➛ helps to express our emotions and interpersonal attitudes,
➛ helps to convey power, affection, dominance, respect etc,
➛ manage and regulate the interaction with others, and
➛ allows self-presentation
प्रश्न मौखिक संप्रेषण को प्रभावी बनाने के लिए सुझाव दीजिये |
मौखिक संप्रेषण को प्रभावी बनाने के लिए कुछ सुझाव दिए गए है:
➛ पढ़कर और सुनकर भाषा को सुधारिए।
➛ बोलने के ढंग, शैली व उच्चारण पर कार्य कीजिए।
➛ पहले सोचिए फिर बोलिए।
➛ ज्यादा जल्दी व जोर से न बोलिए।
➛ दूसरी संस्कृति के अतिसंवेदनशील शब्दों, चिन्हों व सन्दर्भो को सीखिए।
How non-verbal communication helps
Given below are tips on how verbal communication can be made more effective:
➛ Improve language by reading and listening;
➛ Work on voice modulation, tone and pronunciation;
➛ Think and then speak;
➛ Do not speak fast or too loudly;
➛ Learn about culturally sensitive words, signs and contexts for different cultures.
प्रश्न अभिवृत्ति के कार्यों का संक्षिप्त वर्णन करें। अपने उत्तर को उदाहरण के साथ लिखें।
हम अभिवत्तियों का निर्माण क्यों करते हैं? यह सामाजिक जीवन का सरलीकरण करती हैं, जो बहत जटिल होती हैं और अलग-अलग प्रकार की जानकारी से भरी होती है।
प्रश्न अभिवृत्ति हमारे जीवन में चार महत्वपूर्ण कार्य करती हैं –
1. अभिवृत्तियाँ हमें अपने आस-पास के संसार को समझने देती हैं। सकारात्मक अभिवृत्तियाँ
हमें कुछ लोगों के पास जाने में तथा उनकी बात मानने में सहायता करती हैं। आप अपने को आदर्श व्यक्ति के साथ पहचान सकते हैं (जैसे- सचिन तेंदुलकर, मदर टेरेसा) और इन्हीं की तरह सोचने व व्यवहार करने का ढंग अपनाने का प्रयास कर सकते हैं। नकारात्मक अभिवृत्तियाँ हमें ऐसे लोगों व स्थितियों से दूर रखती हैं।
2. अभिवृत्तियाँ सामाजिक समूहों का वर्णन करने में सहायता करती हैं, जिनसे हम में से प्रत्येक व्यक्ति सम्बन्ध रखता है। परिवार, मित्र समूह, धर्मिक या राजनीतिक समूह के सदस्य होने के कारण हम एक जैसी अभिवृत्तियाँ रखते हैं जो हमें एक साथ जोड़े रखने में सहायक होती हैं। इसीलिए शायद हम जिस सामाजिक और राजनीतिक समूह से सम्बन्ध रखते हैं उनके प्रति अनुकूल व दूसरे समूहों के प्रति प्रतिकूल अभिवृत्ति प्रस्तुत करते हैं।
3.अभिवृत्तियाँ हमें हम कौन हैं या अपनी पहचान को समझने में भी सहायक सिद्ध होती है।अभिवृत्तियाँ मूल्यों तथा आत्म-संप्रत्यय को व्यक्त भी करती हैं। उदाहरण के रूप में, कुछ लोग एकता को अधिक महत्व देते हैं और वहीं कुछ लोग स्वतंत्रता या करुणा को अधिक महत्व देते हैं। ईमानदारी के प्रति महात्मा गांधी की अभिवृत्ति एवं गरीबों तथा जरूरतमंदों के प्रति मदर टेरेसा की चिन्ता सर्वविदित है।
4. अभिवृत्तियाँ हमें दूसरों से सहायता, प्रशंसा व स्वीकृति प्राप्त करने में भी सहायक होती हैं। समान अभिवृत्तियों वाले व्यक्ति एक दूसरे की ओर आकर्षित होते हैं। उदाहरणतः आप और आपका दोस्त एक जैसी रुचि व अभिवृत्ति रखते हैं, आप दोनों एक-दूसरे को पसन्द भी करते हैं और इसलिए अपनी दोस्ती को बनाये रखना आपके लिए आसान है। इस प्रकार अभिवृत्तियाँ हमें अपनी सामाजिक अन्तःक्रिया में सहायता करती हैं।
Briefly describe the functions of attitudes. Illustrate your answer with examples.
Why do we form attitudes? It allows us to simplify social life which is complicated and full of various types of information. Attitudes serve four important functions in our lives:
1. Attitudes allow us to understand the world around us. Positive attitudes help to come closer to some people and make you agree to their requests. You may identify with role models (e.g. Sachin Tendulkar, Mother Teresa) and try to develop their way of thinking and behaving. The negative attitudes make us stay away from such people or situations.
2. Attitudes help describe the social groups that each one of us belongs to. As members of a family, group of friends, or, religious, political group we share similar attitudes and this helps to bind us together. Thus we may favour the religious and political groups we belong to and show unfavourable attitude towards the other groups.
3. Attitudes also help us to understand ‘who we are’ or our identity. Attitudes express an individual’s values and self-concept. For example, some people value equality while others may value freedom or compassion. Mahatama Gandhi’s attitude towards honesty and Mother Teresa’s concern for the poor and needy is well known.
4. Attitudes help us to get support, praise and acceptance from others. People who hold similar attitudes are attracted toward each other. For example, your friend and you share common interests and attitudes, both of you like each other and hence it makes easier to carry on the friendship. Thus attitudes help us to adjust in our social interaction.
प्रश्न प्रसन्नता और सुख को कितने तरीकों से प्राप्त किया जा सकता है ?
प्रसन्नता और सुख को कई तरीकों से प्राप्त किया जा सकता है
1. भौतिक संसाधनः धन, वस्त्र और मकान हमारी मूलभूत आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करते हैं।
विभिन्न आवश्यकताओं और उनके स्वरूप को पिछले पाठ में हम पढ़ चुके हैं। खुश रहने के लिए हमें अपनी प्राथमिक और गौण आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करना आवश्यक है।
2. संज्ञानात्मक सामर्थ्यः अपनी आवश्यकता की वस्तु खोजने और पाने की योग्यता भी महत्वपूर्ण है। इसलिए हमें सुविज्ञ, बुद्धिमान, सीखने की ओर अग्रसर रहना चाहिए।
3. व्यक्तिपरक योग्यताः अपनी समस्याओं का समाधान करने की क्षमता पर हमारा विश्वास, हमें आत्मविश्वास और अपने लक्ष्य को प्राप्त करने की सामर्थ्य पर भरोसा देता है।
In how many ways can happiness and happiness be achieved?
Pleasure and happiness can be achieved in many ways
1. Material Resources: Money, clothes and houses fulfil our basic needs.
We have read about various needs and their nature in the previous lesson. To be happy, we need to fulfill our primary and secondary needs.
2. Cognitive ability: The ability to find and get what we need is also important. That is why we should be intelligent, intelligent, moving towards learning.
3. Subjective Ability: Our belief in our ability to solve our own problems gives us confidence and confidence in our ability to achieve our goals.
प्रश्न आत्म-यथार्थीकृत व्यक्तियों की शक्तियों को पहचानना |
➛ आत्म-निरीक्षण या अपने व्यवहार को स्वयं के प्रति व दूसरों के संबंध में जांचना।
➛ आत्मस्वीकृति, आत्मसम्मान और आत्मविश्वास। प्रभावशाली संप्रेषण कौशल।
➛ सकारात्मक दृष्टिकोण : विफलता का सामना करना और गलतियों से सीखना।
➛ उद्देश्यपूर्ण जीवन या किये गये कार्य में अर्थ ढूंढना।
➛ वास्तविक लक्ष्यों को निर्धारित करके अपनी योग्यताओं और कौशल का सर्वश्रेष्ठ उपयोग करते हुए उन्हें प्राप्त करने के लिए प्रयत्न करना।
➛ परिस्थितियों के अनुरूप ढल जाना
➛ यह विश्वास रखना कि बाधाएं अस्थाई होती हैं और मुश्किल समय सदा के लिए नहीं रहता।
➛ दूसरों से सुदृढ़ एवं गहन संबंध स्थापित करना।
Recognizing strengths of self actualizes individuals
➛ Self-monitoring or examining own behaviour in relation to self and others.
➛ Self-acceptance, self-esteem and confidence in self.
➛ Effective communication skills.
➛ Positive attitude: coping with failure and learn from mistakes.
➛ Purpose in life or finding meaning in what they do.
➛ Set realistic goals and try to achieve them to the best of their ability and skills.
➛ Flexibility or changing according to the demands of the situation.
➛ Belief that setbacks are temporary and short-lived and not going to last for ever.
➛ Relate to others and have deep relationships with others.
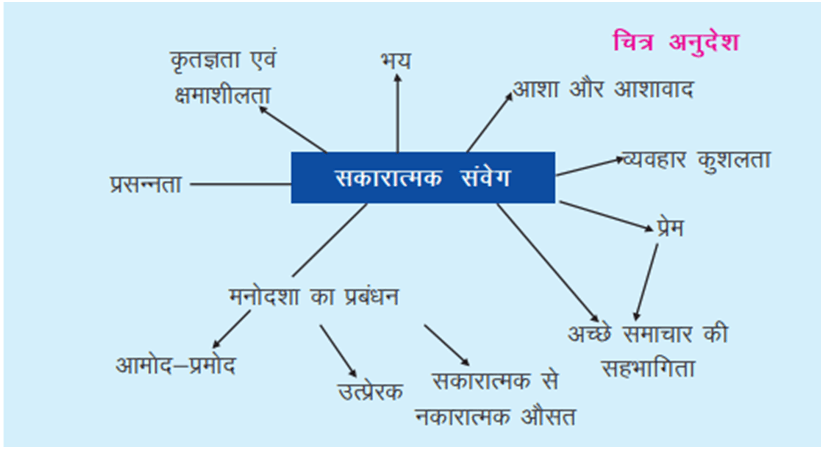
प्रश्न सकारात्मक संवेगों से होने वाले प्रभाव हमारे जीवन में सहायक कैसे होते हैं
सकारात्मक संवेगों से होने वाले प्रभाव हमारे जीवन में सहायक होते हैं क्योंकि
➛ चिन्तन और ध्यान व्यापक और गहन हो जाते हैं परिणामस्वरूप वे संकट से निपटने की नीतियां बनाते हैं।
➛ सकारात्मक संवेग नकारात्मक संवेगों से उत्पन्न होने वाले बुरे प्रभावों का सुधार करते हैं।
➛ मानसिक स्वास्थ्य और सुख में बढ़ोत्तरी करते हैं : इससे हम जागरूकता, उत्साह, दृढ़ निश्चयता और उर्जा को प्रदर्शित करते हैं।
➛ सकारात्मक संवेग दूसरों के साथ मेल-जोल के वैयक्तिक संसाधन बनाते हैं:- हम नये मित्र बनाते हैं और उनके साथ सहभागिता एवं जुड़ाव करते हैं।
➛ आशावादिता, और दृढ़ता निर्माण करते हैं।
➛ सकारात्मक संवेगों को दर्शाने वाले व्यक्ति प्रेम की भावना को अधिक महसूस कर पाते हैं।
➛ प्रसन्नचित्त व्यक्ति अपने कार्यों को प्रभावशाली तरीके से करने व सफलता को प्राप्त करने में ज्यादा सक्षम होते हैं।
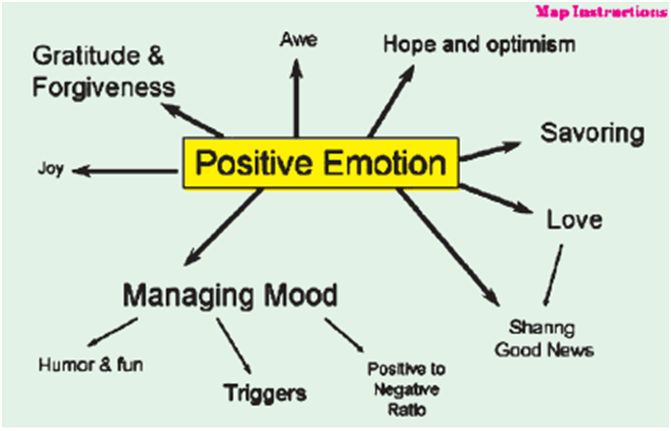
Over time the influence of positive emotions helps because
Attention and thinking are broadened and deepened which in turn builds our coping strategies.
➛ Positive emotions repair the negative effects of negative emotions.
➛ Enhances mental health and well-being: we show alertness, enthusiasm, determination and energy.
➛ Helps build personal resources for interaction with others: we make new friends, we share and bond with them.
➛ Build optimism, tranquility and resilience.
➛ People who show positive emotions are more likely to feel loved.
➛ Happy people are more effective and successful in their work.
प्रश्न सकारात्मक संवेगों को उभारने के उपाय
➛ सकारात्मक संवेगों को निम्नलिखित तरीकों से बढ़ाया जा सकता है:
➛ तनावमुक्त करने वाले व्यायाम जैसे ध्यान और योग करें।
➛ जीवन में सकारात्मक अर्थ को खोजें- नकारात्मक घटनाओं के प्रति दृष्टिकोण बदलें व । उनमें निहित सकारात्मक पहलुओं को पहचानें।
➛ प्रतिदिन की गतिविधियों में प्रसन्नता और संतोष खोजें।
➛ यथार्थवादी लक्ष्यों को खोजें ताकि आपको उपलब्धि का अनुभव हो सके।
➛ रुचि की गतिविधियों को करें।
➛ स्वयं से हटकर दूसरों की सहायता करें।
➛ दूसरों के प्रति कृतज्ञ रहने से आपकी पहचान और जागरूकता विस्तृत होगी।
Ways to Promote Positive Emotions
The ways by which we can enhance positive emotions are:
➛ Do relaxation exercises such as meditation and yoga.
➛ Find positive meaning in life – reframe negative events and view in a positive light.
➛ Find happiness and satisfaction in daily life activities.
➛ Pursue realistic goals so that you get a sense of achievement.
➛ Undertake activities which you love doing.
➛ Focus beyond self and help others as this makes you a happier person.
➛ Show gratitude – when you show gratitude towards others your identity and awareness will be broadened.
प्रश्न किन्हीं 5 मानसिक विकारों को पहचानिए और उनके प्रमुख लक्षणों का वर्णन कीजिए।
➛ घबराहट संबंधी विकार, जिसमें पैनिक डिसऑर्डर, जुनूनी-बाध्यकारी विकार और फोबिया शामिल हैं।
➛ अवसाद, द्विध्रुवी विकार और अन्य मनोदशा संबंधी विकार।
➛ भोजन विकार।
➛ व्यक्तित्व विकार।
➛ अभिघातज के बाद का तनाव विकार।
➛ मानसिक विकार, जिसमें सिज़ोफ्रेनिया भी शामिल है।
Identify any 5 mental disorders and describe their main symptoms.
➛ Anxiety disorders, including panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and phobias.
➛ Depression, bipolar disorder, and other mood disorders.
➛ Eating disorders.
➛ Personality disorders.
➛ Post-traumatic stress disorder.
➛ Psychotic disorders, including schizophrenia.
प्रश्न कमजोर मानसिक स्वास्थ्य के सूचक/लक्षण
मुख्य व्यवहार जो कमजोर मानसिक स्वास्थ्य को दर्शाने वाले सूचक हैं, वे निम्नलिखित हैं:
1. अव्यवस्थित और असंगठित दिनचर्या ।
2 गुस्सैल और चिड़चिड़ा व्यवहार।
3. क्रोधित और आक्रामक व्यवहार।
4. अशांति।
5. बढ़ी हुई या अपर्याप्त भूख और अपच ।
6. अनियमित निद्रा स्वरूप जैसे कि अनिद्रा, अशांत निंद्रा, अत्यधिक निद्रा।
7. कमजोर अंतरवैयक्तिक संबंध।
Indicators/symptoms of poor mental health
(i) Haphazard and disorganized daily life routine.
(ii) Short-tempered and irritating behaviour.
(iii) Anger and aggressive behaviour.
(iv) Restlessness.
(v) Increased or poor appetite and indigestion.
(vi) Irregular sleeping pattern such as insomnia, disturbed sleep, or narcolepsy
(excess sleep).
(vii) Poor interpersonal relationships.
(viii)Anxiety and worry.
प्रश्न कैरियर चयन कैसे करना है ?
➛ “कैरियर-चयन एक साधारण कार्य है।”
➛ “एक कैरियर परामर्शदाता बता सकता है कि किस व्यापार का चयन करना चाहिए।”
➛ “अपने मनपसन्द कार्य से जीविका नहीं चला सकते।” “बहुत सारा धन कमाना हमें प्रसन्न बनायेगा।”
➛ “एक बार एक कैरियर का चयन कर लूँ, मैं उसमें आजीवन रहूँगा।”
➛ “अगर मैं कैरियर बदलूंगा, तो मेरी कौशल बेकार जायेगा।”
➛”यदि मेरे घनिष्ठ मित्र/रिश्तेदार प्रसन्न हैं तो मैं भी प्रसन्न हूँ।”
➛ “मुझे सिर्फ एक व्यापार का चयन करना है।”
➛ “किसी व्यापार पर काम किये बिना मैं उसके बारे में बहुत कम सीख सकता हूँ।”
How to choose a career?
1. “Choosing a career is a simple task”.
2. “A career counselor can tell, what occupation to pick.”
3. “I cannot make a living from my hobby.”
4. “Making a lot of money will make me happy.”
5. “Once I choose a career, I will be stuck in it forever.”
6. “If I change my career my skills will go waste.”
7. “If my best friends/relatives are happy, I will be too.”
8. “All I have to do is to pick an occupation.”
9. “There is very little I can do to learn about an occupation, without actually working on it.”