
➥ Chemistry Questions
Q1.What is quick lime?
Ans. Quick lime is calcium oxide (CaO)
Q2.What is slaked lime?
Ans. slaked lime is calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2
Q3.What is the nature of slaked lime?
Ans. It’s basic by nature.
Q4.What do you observe when water and quick lime is added in a beaker? Can you identify the type of reaction?
Ans. A fast and vigorous reaction place. The beaker becomes hot indicating its exothermic nature. It is an example of a combination reaction.
Q5.Write the basic chemical reaction involved in slaking of lime.
Ans.
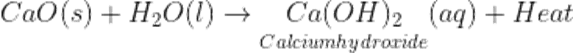
Q6.What is the colour of freshly prepared ferrous sulphate solution? State its common name in hydrated state.
Ans. Its colour is light green. Its called green vitriol.Chemical formula, FeSO4 .7H2O
Q7.What is the colour of ferric sulphate solution?
Ans. It is light brown in colour.
Q8.Name the type of reactions which takes place when ferrous sulphate crystals and calcium carbonate in heated. Write the balanced chemical reaction involved.
Ans. These are decomposition reactions.
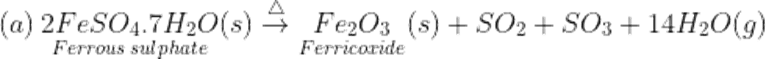
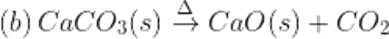
Q9. What is blue Vitriol?
Ans. It is a copper sulphate pentahydrate, CuSO4 .5H2O.
Q10.Can you store copper sulphate solution in iron container?
Ans.No, We cannot store copper sulphate in iron container because iron being more reactive will displace copper and will change to iron sulphate.
Q11.What do you mean by activity series of metals?
Ans. List of metals written in an order where the most reactive metal lies at the top and the least reactive at the bottom,i.e.metals arranged in descending order of their reactivity s called reactivity or activity series of metals.
Q12.Name any two metals which are more reactive than iron?
Ans. Sodium and Aluminum
Q13.What will you observe if the copper filling is added to green colour ferrous sulphate solutions?
Ans. We will observe no change or reaction as iron can’t be displaced by less reactive copper from its salt solution.
Q14. A piece of magnesium is put into copper sulphate solutions. What would be the expected observation?
Ans. The blue colour of (CuSO4) copper sulphate solutions will fade and will finally turn colourless . The magnesium piece will get covered by the red-brown coating.
Q15.If a student is provided with three-piece of metals Zn, Cu and Ag each . Which one he/she will prefer to prepare hydrogen gas using dilute HCl?
Ans. The student will use the piece of Zn metal to produce hydrogen gas as only Zn is more reactive than hydrogen ad thus will displace hydrogen from HCl.
Q16. What is the name of the functional group of acetic acid?
As. Carboxylic acid (-COOH)
Q17.What is vinegar?
Ans. 5 TO 8% solution of acetic acid in water is known as vinegar.
Q18. What causes acidity of acetic acid?
Ans. In aqueous medium acetic acid releases ion, which is responsible for its acidic character.It is a weak acid.
Q19. Mention any two uses of acetic acid in industry.
Ans. (a) It is used as a coagulant in the rubber industry.
(b) Used in the food industry as vinegar.
Q20. What happens when ethanol is added to acetic acid in the presence of sulphuric acid. Write the chemical reaction.
Ans. A sweet-smelling substance, ethyl acetate is formed.(CH3COOC2H5).
Q21.Which gas is evolved when sodium bicarbonate is added to a test tube containing acetic acid?
Ans.Co2,carbondioxide gas
Q22.Why pure acetic acid is called glacial acetic acid?
Ans. Pure acetic acid has freezing point at 16.6ºC ad it floats an water just like glaciers. Thus because of the similarity of appearance its called glacial acetic acid.
Q23.Why do we need to heat the reaction mixture in a water bath during esterification reaction?
Ans. We need to heat the reflection mixture to increase its rate which is otherwise slow. As the mixture contains alcohol, it is highly inflammable, hence we use water bath.
Q24.What is the need to add concentrated sulphuric acid in esterification reaction?
Ans. Concentrated sulphuric acid acts as a catalyst to increase the rate of reaction. Also, it’s a dehydrating agent ad so it absorbs by-product water, keeping the rate of reversible reaction in more ad more forward direction.
Q25. What makes water hard?
Ans. The presence of Ca²+ and Mg²+ salt in water make it hard.
Q26. What is hard water?
Ans. Water which does not form a good lather with soap solution is called hard water.
Q27. A student adds 1ml of soap solution in 5ml of water. He observes a foamy appearance inside the test tube. What does this signify?
Ans. The foam produced by the soap signifies good lather formation indicating softness of the water taken in the test tube.
Q28.If a soap solution is prepared in alcohol (ethanol) rather than water can we use that solution for cleaning grease from a piece of cloth?
Ans.In alcohol soap will be completely soluble, hence micelle formation will not take place which will hamper the cleansing action of soap. On the other hand alcohol will itself dissolve some grease and may clean the piece of cloth.
Q29.Define the temporary hardness of water?
Ans. The presence of calcium or magnesium in the form of bicarbonates causes temporary hardness of the water.
Q30.Why its called temporary hardness?
Ans. It is called temporary hardness as it can be easily removed by the boiling the hard water following by filtration or sedimentation.
On boiling the bicarbonates decompose into insoluble carbonates which can be separated by filtration.
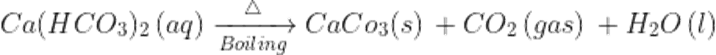
Q31. How permanent hardness of water can be removed?
Ans. Permanent hardness of water ca e removed by boiling it with sodium carbonate(Na2CO3) or washing soda.O boiling the chlorides ad sulphates will covert to insoluble carbonates which ca e removed y filtration or sedimentation.
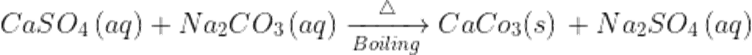
Q32.While conducting the experiment for hard water. Which will form more form, soap, or detergent?
Ans. The detergent will form more foam. Soap will form less foam but scum.
Q33.What is the role of HCl in the stomach?
Ans. HCl in the stomach is released by its wall and has two important functions.
(i) HCl kills the bacteria that exist in the food we have taken.
(ii) The main role of HCl is to maintain the pH value of the stomach suitable for the secretion of the enzymes
➥ Biology Questions
Q1.What is the function of guard cells in stomata?
Ans. The guard cells regulate/control the opening and closing of stomata.
Q2.Why are stomata absent in roots.
Ans. As a little gas exchange takes place in roots hence stomata are not present in them.
Q3.Each stoma is surrounded by two bean-shaped cells. What are they called?
Ans. They are called guard cells.
Q4.Which surface of dicot leaves more stomata are present?
Ans.On the lower surface of leaves i.e lower epidermis.
Q5.What is transpiration?
Ans. The loss of water in the form of vapours from the surface of leaves is called transpiration.
Q6. How will one identify monocot leave and a dicote leave on the basis of stomata?
Ans. Guard on the monocot leaves are dumb-bell shaped while in dicot leaves they are kidney-shaped or bean-shaped.
Q7.Which side of leaves should be observed for stomata in dicot plants?
Ans. Stomata is present in both sides of the dicot leaf.
Q8.What are the function of the stomatal apparatus?
Ans. The function of the stomata are:
(a) For the exchange of gases during respiration and photosynthesis.
(b) During transpiration for loss of water.
Q9. Do the guard cells have rigid or elastic walls? Justify your answers.
Ans. Guard cells have thicker cell walls on inner side than the outer side. This adds to their flexibility while opening and closing.
Q10.Define venation.
Ans. The pattern of veins in a leaf lamina is called venation. Some plants monocots have parallel venation and others (dicots) have network type venation(reticulate).
Q11. State the difference between photosynthesis and respiration.
Ans.
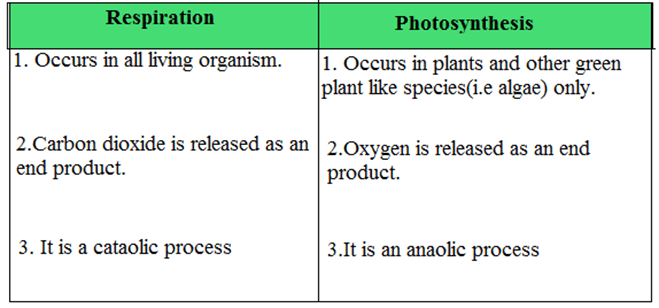
Q12. What do you mean by a catabolic process?
Ans. Catabolism means the metabolic activities which involve breakdown of complex substances like glucose in cells is broken simpler substances(H2O & CO2).
Q13.Define breathing.
Ans. The physical process of inhalation of oxygen and exhalation of carbon dioxide is called breathing.
Q14.Define fermentation.
Ans.It is a type of anaerobic respiration. It also releases CO2 as a by-product.
Q15. Why we use germinating seeds but not green leaves of a plant to demonstrate respiration.
Ans. Germinating seeds are under rapid growth hence they actively respire. On the other hand, green leaves of a plant will undergo photosynthesis also along with respiration. Thus it will utilize CO2 produced during respiration, hence the presence of CO2 may not be detected properly.
Q16. What is the role of KOH in this experiment?
Ans.KOH absorbs the CO2 produced thus creating a partial vacuum in the flask.
Q17.Why germinating seeds are moistened so that they don’t dry up and continue respiration with the help of moisture.
Ans. The seeds are moistened so that they don’t dry up and continue respiration with the help of moisture.
Q18.What are raw materials for respiration?
Ans. Sugars and oxygen.
Q19. What is the full form of ATP.
Ans. Adenosine Triphosphate, it is an energy-rich molecule.
Q20. What is asexual reproduction?
Ans. It is a mode of reproduction in which a single organism produces new organisms without the formation of ay special cell(gamete). A single parent produces two or more individuals.
Q21.Define fission and type of fissions.
Ans. A mode of reproduction when an organism divides into two or more off sprigs. The parent organism splits into two or more off sprigs. The parent organism splits into two or more parts. Fission is of two types.
(a) Binary fission: Organism divides into two daughter cells.
(b) Multiple fission: Organism divides into two or more than two individuals.
Q22.Name an organism which divides by multiple fission,
Ans. Plasmodium (Malaria parasite)
Q23.How many fissions occurs in Amoeba?
Ans. A mature cell of amoeba undergoes karyokinesis(i.e division of nucleus first followed by cytokinesis (i.e division of the cytoplasm) resulting in the formation of two daughter cells. The parent amoeba cell loses its identity in such division.
Q24.What is vegetative propagation?
Ans. Growing of plants from vegetative parts of it like leaf, root, or stem is known as vegetative propagation. It is an asexual mode of reproduction.
Q25. Is budding in yeast different from hydra? Justify your answer.
Ans. In yeast, budding occurs in the form of a protuberance on the parent yeast cell. It may separate or may not separate and can further develop into several daughter buds. In hydra, the bud separates due to repeated mitotic cell division and is a multicellular single organism itself.
Q26.Which type of cell division involved in binary fission?
Ans. Mitosis, as the number of chromosomes, remains the same.
Q27. Mention the points of differences between sexual ad asexual reproduction.
Ans.
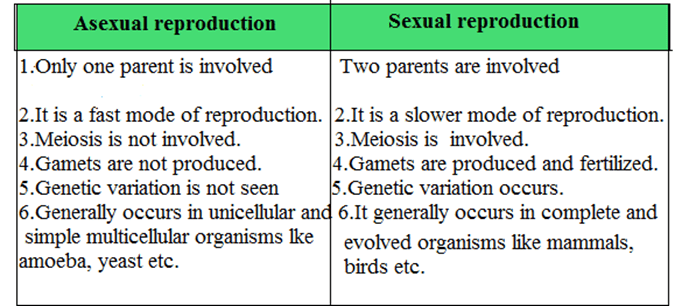
➥ Physics Questions
Q1. State Ohm’s law.
Ans. Ohm’s law states that if physical conditions like temperature remain constant or same the current(I) flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference(V) applied across the ends.
i.e V ∞ I
or V = IR Where R = resistance of the conductor
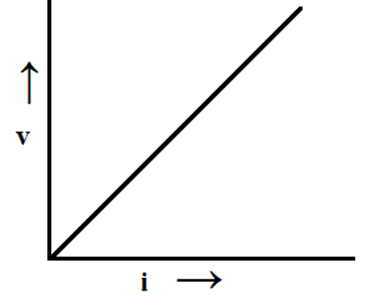
Q2. Is Ohm’s law true for all material?
Ans. It doesn’t hold good for electronic devices and non-ohmic resistance. Like semi-conductor diodes.
Q3.what is meant by E.M.F and potential difference of a cell
Ans. The maximum potential difference which exists between the terminals of a cell when no current is drawn from the cell is called e.m.f. (electromotive force)of the cell. On the other hand, when current is being drawn from the cell, the potential difference which exists between or across the terminals is called terminal potential difference or potential difference.
Q4.Define the potential difference. State whether the potential difference of a cell is smaller than its e.m.f.
Ans.The amount of work done when a single unit charge (1 coulomb) flows from one point to another point in a circuit.
Potential difference is smaller than e.m.f. is used in overcoming the internal resistance of a cell when current is drawn from it.
Q5.What is electric current?
Ans. The rate of flow of charge or electrons through a conductor is called electric current. Its SI unit is ampere (A).
Q6.Why copper wire is used in electric circuits?
Ans. Copper metal is a very good conductor of electricity. It has many free electrons to conduct current. It is not very expensive also.
Q7.What is an ammeter? What do you mean by its least count?
Ans. An ammeter is an instrument to measure the magnitude of electric current flowing in a closed circuit. An ammeter is always connected in series.
By least count of any device or instrument, we mean the minimum quantity of the scale which can be read accurately in that instrument. For an ammeter, the least count is the minimum amount of current it can measure.
Q8.What is the battery eliminator?
Ans. A battery eliminator converts AC current to low voltage DC current.
Q9.What is voltmeter?
Ans. Its an instrument used to measure the potential difference across two points in a circuit carrying current.
Q10.Why a voltmeter is always connected in parallel?
Ans. A voltmeter has a very high resistance, hence it will allow a small amount of current it in a parallel circuit thus it will not interfere with the correct circuit measurements.
Q11.Define resistance.
Ans. The obstruction or oppose to the normal flow of current by the conductor when current is flowing through it is called resistance. Its SI unit is ohm(Ω).
Q12.What is the effect of temperature on the resistance of a conductor?
Ans. The resistance of most of the metallic conductors increases with an increase in temperature.
Q13.State the relationship of length and surface area of a conductor with its resistance.
Ans. Resistance is directly proportional to the length of conductor and inversely proportional to the area of cross-section.
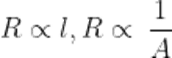
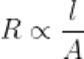
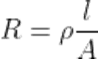
Where, R = resistance(Ω), l= legth of the conductor(in meter), A= area of cross-section in m²
ρ = resistivity (Ohm-meter)
Q14.What is the drawback if lights (lamps) are connected in series?
Ans. The main drawback is that if one lamp fuses the rest of the lamps will also stop functioning as current supply will stop functioning as the current supply will stop or get disconnected.
Q15.Why are we advised to remove the plug from the key as soon as readings or observations are noted down?
Ans. We are advised to do so because longer duration of flow of current through the circuit will cause heating of the conductor wire thus increasing its resistance, which will provide an error in readings.
Q16. Is the equivalent resistance of parallel combination greater than the individual resistance?
Ans.No, its value is smaller than the individual resistance if placed in series or separately.
Q17.Why rheostat of low resistance is used?
Ans. A rheostat of low resistance keeps the option open for a large variation in resistance thus cause a variety of current flow in the circuit to take many readings.
Q18.If two resistors having resistances of 3Ω and 4Ω respectively are connected in parallel, what will be the net resistance in the circuit?
Ans. The given resistors are of 3Ω and 4Ω
Let the net resistance of both is R, then calculating the net resistance as following.
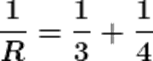
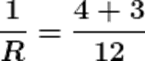
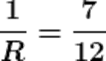
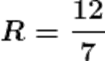
R ≈1.71 Ω
Therefore the net resistance of the circuit is almost 1.71 Ω
Q19.What happens to the ray of light which passes through the optical center of the lens.
Ans. The ray of light which passes through the optical center of a lens, doesn’t deviate from its path.
Q20. State the nature of the image formed when an object is placed between F1 and F2 in front of the biconvex lens.
Ans. The image will be formed beyond 2F1 and it will be real, inverted, and magnified.
Q21. Define the angle of deviation.
Ans. In the refraction of a light ray, the angle between the incident and emergent rays is known as angle of deviation.
Q22. Define the angle of emergent ray.
Ans. The ray of light after undergoing refraction within the glass prism emerges out from the opposite face of the prism from where it entered is called the emergent ray.
Q23.What is the drawback if lights (lamps) are connected in series?
Ans.The main drawback is that if one lamp fuses the rest of the lamps will also stop functioning as current supply will stop functioning as the current supply will stop or get disconnected.
Q24.Why are we adviced to remove the plug from the key as soon as readings or observations are noted down?
Ans.We are advised to do so because longer duration of flow of current through the circuit will cause heating of the conductor wire thus increasing its resistance,which will provide an error in readings.
Q25.Is the equivalent resistance of parallel combination greater than the individual resistance?
Ans.No,its value is smaller than the individual resistance if placed in series or separately.
Q26.Why rheostat of low resistance is used?
Ans.A rheostat of low resistance keeps the option open for a large variation in resistance thus cause a variety of current flow in the circuit to take many readings.
Q27.Why are the incident and emergent rays parallel to each other in case of a rectangular glass slab?
Ans.As angle of incidence ∠i is equal to angle of emergence,hence ∠e both the rays are parallel to each other.
Q28.State snell’s law of refraction?
Ans. According to snell’s law,the ratio of the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant, for a light ray of a given colour and for a given pair of media.
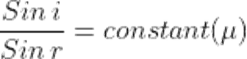
µ = constant,also known as refractive index.μ
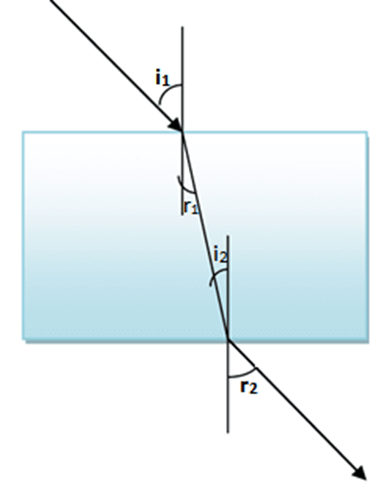
Q29.What is lateral displacement of light?
Ans. lateral displacement is the distance by which an incident ray get shifted sideward while emerging out naturally without any bending or shifting. Its angle of refraction will be zero.
Q30.A ray of light is incident on a glass slab normally. What will happen to the emergent ray?
Ans. There will be no deviation of the path and the emergent ray will be the same as the incident ray, emerging out normally without any bending to shifting. Its angle of refraction will be zero.
Q31. A ray of light traveling in a denser medium meets the surface of a rarer medium. How will it bent?
Ans.The ray while entering the second (rarer) medium at the point of the incident will bend away from the normal.
Q32. Define the angle of deviation.
Ans. It is the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray, it is denoted by ‘d’ or D or ∂.
Q33. Which colour has the longest wavelength in VIBGYOR?
Ans. Red color.
Q34. Which color bend the most while emerging out after dispersion through a prism?
Ans. Violet colour.
Q35.What causes dispersion?
Ans. Different colours have different velocities while passing through a glass medium. They have different refractive indices(µ) . Hence the degree to which each color deviates inside the prism is also different. Hence a beam of white light undergoes dispersion.
Q36. State the relationship between ∠i (incident angle) and ∠A(angle of prism) of an optical glass prism.
Ans. ∠i + ∠e = ∠A + ∠δ
Where ∠i = angle of incidence, ∠e = angle of convergence, ∠A = angle of prism, ∠δ =angle of deviation
Q37. Can you explain why no dispersion is observed in case of a refraction of light through a glass slab?
Ans. A glass slab is a combination of two equal sizes and shaped prism oppositely arranged at their surfaces. Here a ray of light first gets dispersed within the slab but again recombine from its constituent colours to single beam of white light while emerging out.
Q38. In an equilateral prism, determine the angle of emergence, if the angle of incidence is 30°, and the angle of deviation is 28°.
Ans. The relationship between incident angle ∠i, angle of deviation ∠δ, angle of emergence ∠e, and angle of the prism ∠A is given by
Since the prism is equilateral, so the angle of prism ∠A = 60°
∠i + ∠e = ∠A + ∠δ
We are given incident angle ∠i = 30°, angle of deviation ∠δ=28°
30° + ∠e = 60° + 28°
∠e =88° – 30° = 58°
Therefore angle of emergence is = 58°
Q38.Where should an object be placed in order to get a virtual image by a convex lens?
Ans. In order to get a virtual image, the object should be placed between the optical center and the focal point of the convex lens.
Q39.Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get its real and enlarged image?
Ans. The object should be placed at the point beyond the focal point of the convex lens for getting a real and enlarged image.
Q40. What is the resistivity or specific resistance of the material of the conductor?
Ans. Specific resistance or resistivity of a conductor is defined as the resistance of a conductor of a unit length and unit cross area. Its unit is ohm-meter.
Q41. What is equivalent resistance?
Ans. The equivalent resistance is the final resultant resistance offered by a group of resistance when placed in series or parallel combinations.
Q42.Find out the equivalent resistance of resistors 1Ω, 3Ω and 2.5Ω when that are placed in series.
Ans. Let the net resistance is R
R = 1 + 3 + 2.5 = 6.5Ω
Q43. What is the nature of the image formed by the plane mirror?
Ans.Virtual and erected
Q44.What type of image is formed by the convex lens?
Ans. Virtual and magnified when the object is placed between the optical center and focal point and real and inverted when the object is placed at other points on principal focus.
Q45.A point object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 40 cm, determine the distance of the image created by it from the mirror.
Ans. The distance of the object from the mirror ,u = -40 cm
The focal length of the convex mirror,f = 40 cm
Let the distance of the image formed from the mirror is = v
Using the mirror formula.
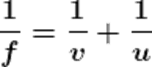
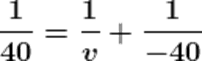
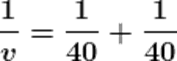
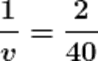
v = 20
Therefore, the image of the mirror will be formed at a distance of 20 cm behind the mirror
Q46. A concave mirror of focal length 15 cm can form a magnified, erect as well as an inverted image of an object placed in front of it . Justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror in both the cases for obtaining the images.
Ans. For obtaining the magnified and erected image the object is placed between the focal point and the pole of the mirror and for obtaining the magnified and erected image the object is placed at the focal point or between the focal point and the pole.
Q47. What is the function of the retina in the human eye?
Ans. The retina in the human eye acts as a screen on which the image of the object is formed, the retina is made of light-sensitive cells known as rods and cones, these cells transform the image into electrical signals and then transported to the brain through the optic nerve and then the inverted image of the object is decoded by the brain to form erected image.